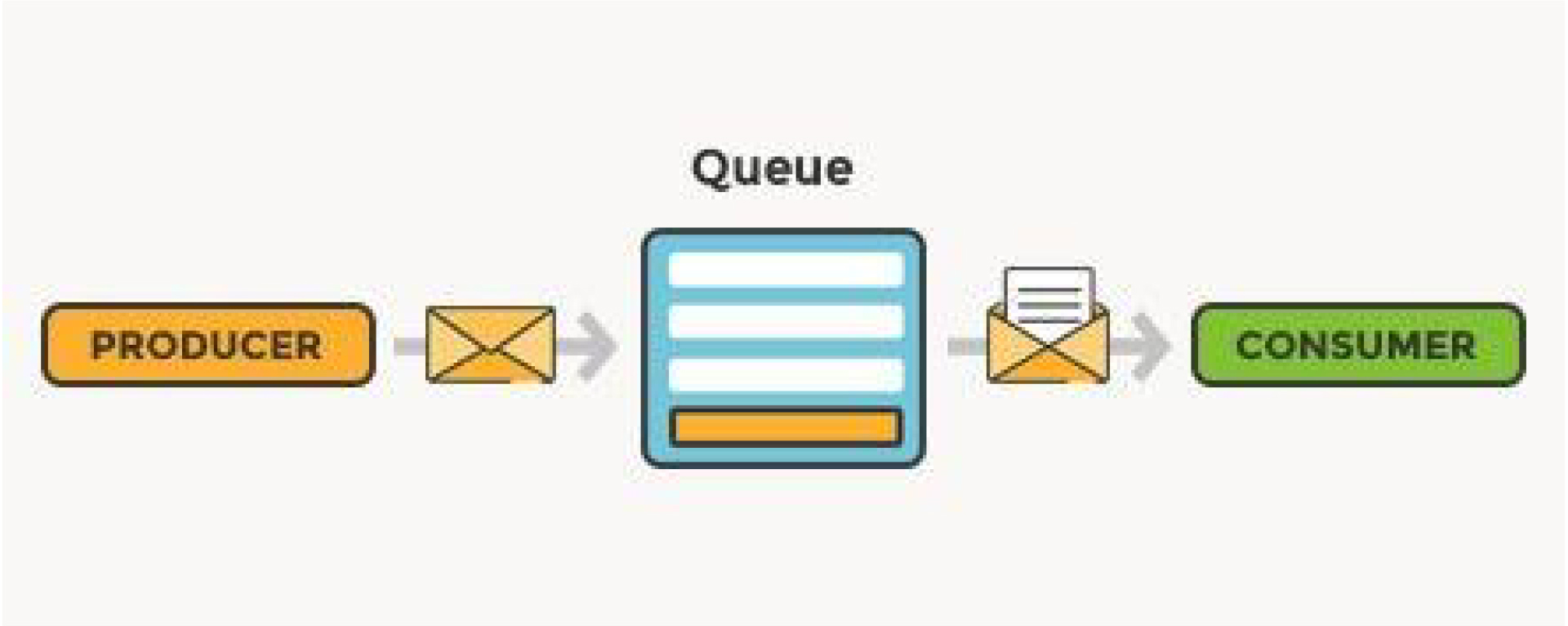
- What is a messaging queue ?
- Messaging queue is a process of sharing the data asynchronously between two or more services.
- The software that puts messages into a queue is called a message producer.
- The software that retrieves messages from the queue is called a message consumer.
- A queue is like a buffer (size of memory space). You can put messages into a queue, and you can retrieve messages from a queue. Messaging queue stores data in FIFO.

When should we use the messaging queue ?
-
- Decoupling architecture
- Message queues help in decoupling parts of the system, allowing different services or components to communicate without having direct dependencies.
- This means that services can operate independently and evolve without impacting each other as long as they follow the messaging format.
- Load Balancing and Scaling
- A queue can act as a buffer, balancing the load by managing the rate of messages sent to consumer services.
- Producers and consumers can scale independently according to workload.
- Since the services are decoupled, we can scale them independently based on demand.
- Reliability and Resilience
- If a consumer goes down, messages can stay in the queue until it’s back-up, ensuring that no data is lost.
- This makes the system more fault-tolerant and resilient to crashes or downtime.
- Decoupling architecture
- Benefits of Message Queues
- Fan-out
- The Payment Service broadcasts a message to a queue for multiple downstream services each independently consumes and processes the data it needs.
- Reduces the producer’s workload, since it doesn’t manage direct communication.
- Increases system scalability and flexibility, as each service can process messages based on its own requirements.
- Data Persistence
- Queues can also be used as middleware that stores messages.
- If the producer service crashes, the consumer service can always pick up the messages from the message queue to process.
- Persisting data in a messaging queue typically requires trade-offs between latency and durability.
- Dead-Letter queues
- When producers produce a message to the queue but due to some failure the consumer cannot consume it (API Failure, Data Format Errors etc.)
- A DLQ is used to handle messages that cannot be processed successfully.
- When messages repeatedly fail processing, they can be sent to a DLQ rather than endlessly retrying.
- Messages in DLQ can be reprocessed later, manually corrected, or moved back to the main queue if the issue is resolved.
- Fan-out
Related Posts
October 30, 2025
Empowering Business Analysts: How AI is Revolutionizing Agile Practices
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, Agile methodologies are no longer optional— they're essential for organizations…
October 30, 2025
What is SAP? How does it work?
The full form of "SAP" is “Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing” which is…
October 3, 2025
Optimizing React Performance: An Advanced Guide for Scalable Applications
In today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem, software systems have become the backbone of every enterprise’s technological…
October 3, 2025
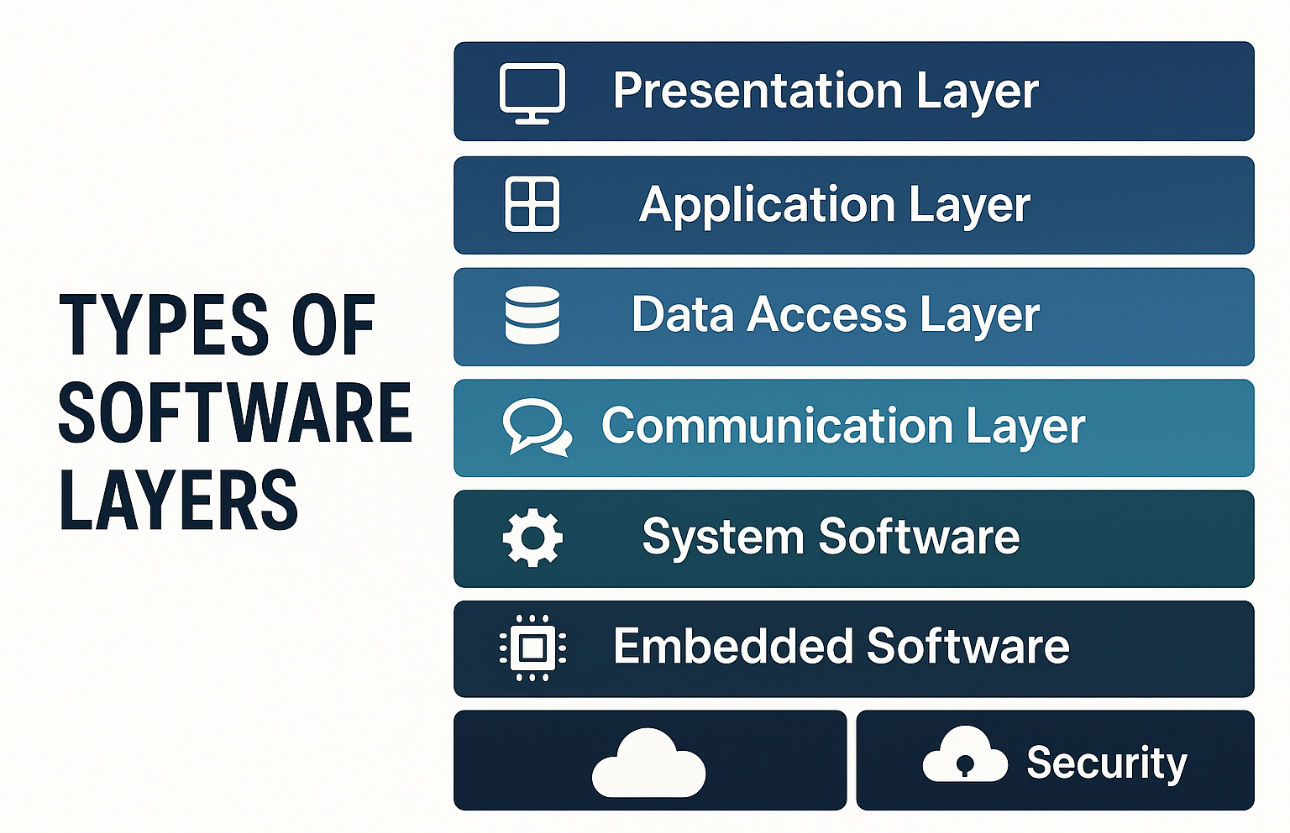
Types of Software Layers
In today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem, software systems have become the backbone of every enterprise’s technological…