In today’s fast-paced digital world, real-time data processing is crucial, and edge computing is revolutionizing how we manage and process data. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which processes data in centralized data centers, edge computing brings computation closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing processes data locally on devices or edge servers, enabling faster decision-making, enhanced bandwidth efficiency. By analyzing data near its source, it reduces reliance on cloud networks, minimizes data transfer costs, and ensures real-time responses, crucial for technologies like self-driving cars. This approach is especially beneficial for remote locations with limited bandwidth, offering better privacy and reducing risks of data corruption during transmission.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes the time taken to process data by performing computations near the data source. This results in real-time or near-instantaneous decision-making, essential for applications like self-driving cars and industrial machinery.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need to send large volumes of data over networks to the cloud, freeing up bandwidth and reducing costs, especially in remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Reliability: Edge computing ensures that data processing continues even if there are issues with connectivity to the cloud, which helps in maintaining continuous operations in critical environments.
Applications of Edge Computing:
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles require and produce anywhere from 5 TB to 20 TB per day, gathering information about location, speed, vehicle condition, road conditions, traffic conditions, and other vehicles. The data must be aggregated and analyzed in real time while the vehicle is in motion. This requires significant onboard computing—each autonomous vehicle becomes an “edge.” Additionally, the data can help authorities and businesses manage vehicle fleets based on actual conditions on the ground.
- Improved Healthcare: The healthcare industry has dramatically expanded the amount of patient data collected from devices, sensors, and other medical equipment. That enormous data volume requires edge computing to apply automation and machine learning to access the data, ignore “normal” data, and identify problem data so that clinicians can take immediate action to help patients avoid health incidents in real time.
- Smart Cities: In smart cities, edge computing helps manage traffic flow, monitor public spaces, and optimize energy consumption by processing data from sensors and devices in real time.
- Retail: Retail businesses can produce enormous data volumes from surveillance, stock tracking, sales data, and other real-time business details. Edge computing can help analyze this diverse data and identify business opportunities, such as an effective endcap or campaign, predict sales and optimize vendor ordering, and so on. Since retail businesses can vary dramatically in local environments, edge computing can be an effective solution for local processing at each store.
Challenges:
- Complex Management: Managing multiple edge devices can be more complex than relying on a centralized cloud-based system, requiring sophisticated management tools and protocols.
- Security Concerns: While edge computing enhances security in some ways, it also introduces new challenges, as the edge devices themselves may be vulnerable to attacks or physical tampering.
- Limited Computational Power: Edge devices generally have limited processing capabilities compared to centralized cloud servers, which may restrict the types of tasks that can be performed at the edge.
Conclusion:
Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing by enabling faster, more efficient, and secure applications, making it essential for IoT, AI, and real-time systems. Despite challenges like limited computational power and complex management, its advantages in reducing latency, optimizing bandwidth, and ensuring reliability make it a pivotal technology. With the rise of 5G, edge computing will unlock new possibilities, offering smarter solutions for industries such as healthcare and manufacturing, while empowering real-time insights and smarter decision-making in an increasingly connected world.
Related Posts
Empowering Business Analysts: How AI is Revolutionizing Agile Practices
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, Agile methodologies are no longer optional— they're essential for organizations…
What is SAP? How does it work?
The full form of "SAP" is “Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing” which is…
Optimizing React Performance: An Advanced Guide for Scalable Applications
In today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem, software systems have become the backbone of every enterprise’s technological…
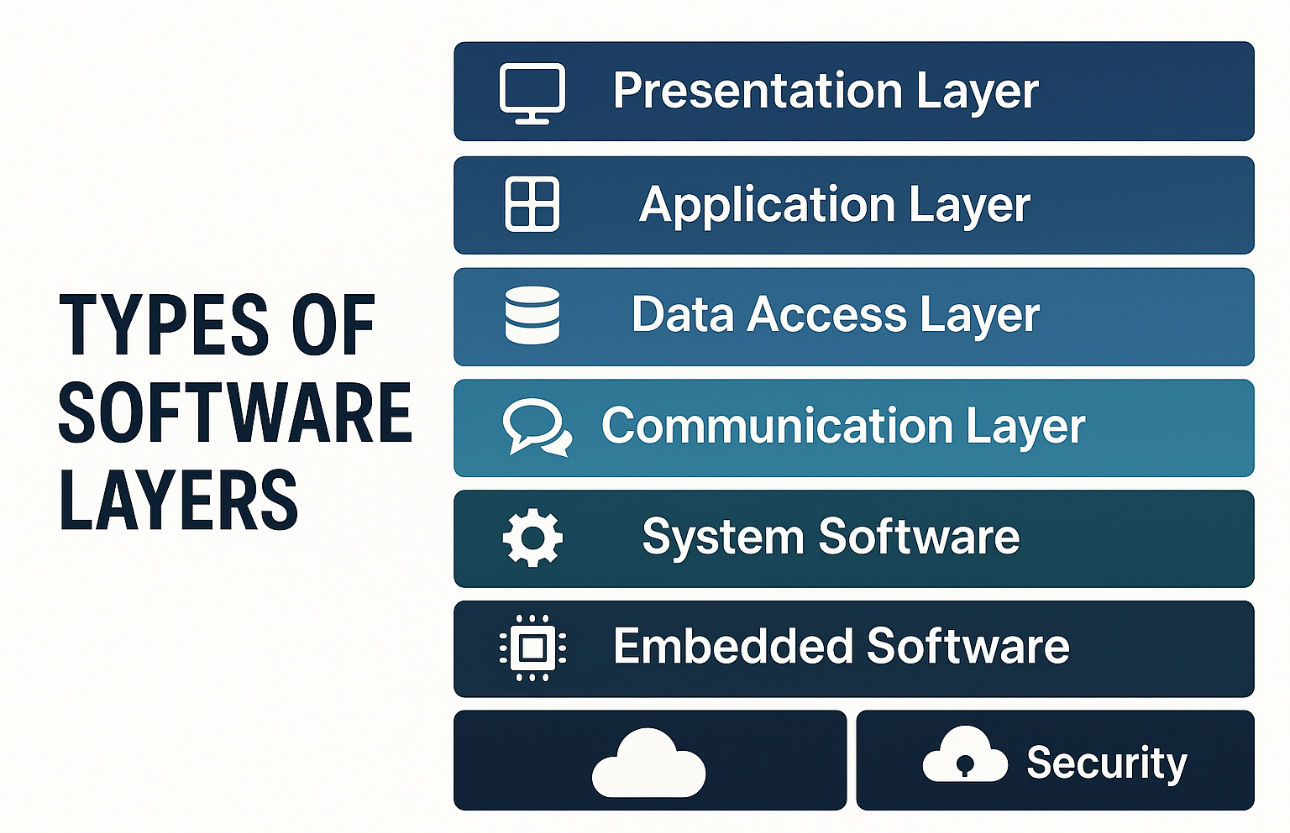
Types of Software Layers
In today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem, software systems have become the backbone of every enterprise’s technological…